Open source 3D printing and 3D printers – RepRap 3D printers
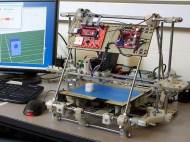 We already published various articles about 3D printers and 3D printing, but we always delayed the publication of the article about the first of the low-cost 3D printers projects whose blueprints and software are publicly available and open source. Named Replicating Rapid-prototyper (RepRap), the 3D printer is practically able to self-replicate since it can print most of its own parts.
We already published various articles about 3D printers and 3D printing, but we always delayed the publication of the article about the first of the low-cost 3D printers projects whose blueprints and software are publicly available and open source. Named Replicating Rapid-prototyper (RepRap), the 3D printer is practically able to self-replicate since it can print most of its own parts.
RepRap was conceived back in February 2004 by Adrian Bowyer, and it represents a modular low-cost version of 3D printers which is able to build the parts up in layers of plastic. Since it is modular and open source (GNU General Public License), it can be modified to use other materials which suite your needs.
Unlike most of other 3D printers, RepRap is able print out half its own parts. The other half consists out of common items which are easily obtainable from hardware stores or on-line, and its developers are finding ways to enable the printer to print some of those more complex parts in order to increase its ability to replicate itself. So, if you have a RepRap machine, you can use it to make another to accelerate the printing process or provide one to a friend or associate.
The cost of materials needed for construction of a RepRap 3D printer is around €400 ($500), making it much more affordable than other 3D printers. That way it’s accessible to small communities in the developing world as well as individuals in the developed world. The only obligation on users is to share their achievements and improvements of the technology in order to enable them to other members of the community.
Although RepRap was initially developed for works in plastic, people have also used it to print in clay, ceramic and silicone rubber. Experiments on getting RepRap to print in low-melting-point metals are at an advanced stage. All these materials can be combined into single complex objects, thus enabling creation of 3D electrical circuitry once the 3D metals printing becomes possible.
The project itself is evolving and there are several versions of the printer which vary in complexity and size, as well as different parts which make it usable with different printing materials. In order to provide the general idea about RepRap’s 3D printing capabilities, here are the specifications of the original Mendel model of RepRap 3D printer. Its overall dimensions are 50x46x41cm (20x16x 14”) and it is able to print object of up to 20x20x11cm (8x8x5.5”). Its accuracy can be up to 0.1mm (depending on the used nozzle) and its building speed can be up to 1,800 mm/min (or 33 cm3/hr regarding Deposition rate).
Pre-soldered electronics with built-in microSD card slot allow standalone printing, and the 3D printers can be directly connected to your computer via USB interface. The software these printers use relies on Python programming language and STL files or Gcodes. For a list of useful software which can be used to create 3D objects and translate them into the form recognizable by the printer, visit this page.
There’s a growing comunity of 3D modelers who share their models on the RapRap Object library page, and you can find inspiration for other 3D object available on Thingiverse website.








Leave your response!