Bionics| Tech»
Virus-templated fabrication of piezoelectric nanogenerators
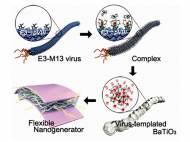 A group of researchers at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) has synthesized a nanogenerator – a flexible piezoelectric energy harvesting device based on biological templates. The biotemplated nanogenerator is low cost and it can be self-powered by simple finger movements that could be used to power small commercial LCD screens and… »
A group of researchers at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) has synthesized a nanogenerator – a flexible piezoelectric energy harvesting device based on biological templates. The biotemplated nanogenerator is low cost and it can be self-powered by simple finger movements that could be used to power small commercial LCD screens and… »