The first photodynamic drug with anti-metastatic activities
 Researchers at the University of Zurich have devised and successfully tested the first potential anticancer drug which has excellent properties as a photodynamic therapy (PDT) agent as well as potential anti-metastatic activities in vivo. Namely, this new agent destroys melanoma skin cancer cells and blocks the spread of the cancer to other sites in the body.
Researchers at the University of Zurich have devised and successfully tested the first potential anticancer drug which has excellent properties as a photodynamic therapy (PDT) agent as well as potential anti-metastatic activities in vivo. Namely, this new agent destroys melanoma skin cancer cells and blocks the spread of the cancer to other sites in the body.
Nathan Luedtke, an associate professor of bioorganic chemistry who led the research, explains that the spread of melanoma and other forms of cancer beyond the original location— a process called metastasis — makes cancer such a serious disease. While surgery is the most suitable treatment option for advanced malignancies, early stage melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancers can be treated with photodynamic therapy which involves utilization a drug that kills cancer cells when exposed to light.
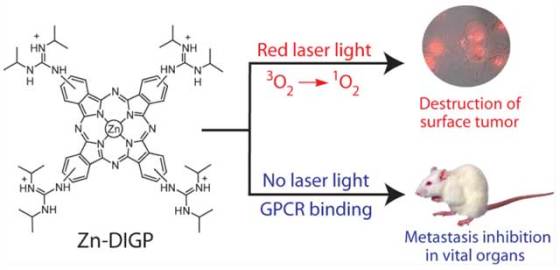
Many photosensitizing agents have been tested in the clinical trials, but none of them showed anti-metastatic activities and had other drawbacks. Luedtke’s team has synthesized tetrakis-(diisopropyl-guanidino) zinc phthalocyanine (Zn-DIGP) that exhibits good cellular uptake and the ability to modulate gene expression. This drug causes low toxicity to cell cultures in the dark, while upon photoexcitation with red laser light Zn-DIGP exhibits large morphological changes and the loss of cellular respiration.
It has been shown that this drug not only killed melanoma cells in laboratory mice, but also stopped them from spreading. According to Luedtke lab researchers, the anti-metastatic activities of Zn-DIGP possibly result from its ability to interfere with chemokine signaling.
These results suggest that Zn-DIGP may serve as multifunctional PDT agents, where light energy can be harnessed for the treatment of surface tumors while inhibiting the formation of new tumor colonies. According to the researchers, this agent provides the first example of a preclinical candidate possessing both of these properties.
For more information, you can read the paper published in ACS Chemical Biology: “Photodynamic Agents with Anti-metastatic Activities” [3.66MB PDF].









Leave your response!